Uploading Your Owm Aws Ami to the Amazon Cloud
What is Amazon Car Prototype (AMI)?
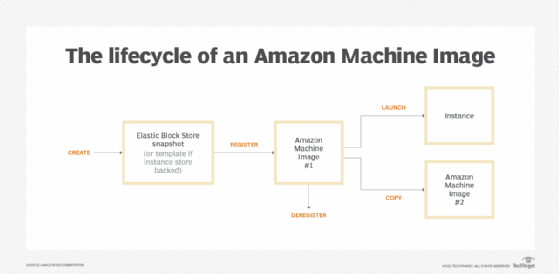
An Amazon Machine Paradigm (AMI) is a master image for the creation of virtual servers -- known every bit EC2 instances -- in the Amazon Spider web Services (AWS) surroundings.
The machine images are like templates that are configured with an operating organization and other software that decide the user's operating environment. AMI types are categorized according to region, operating organisation, arrangement compages -- 32- or 64-bit -- launch permissions and whether they are backed past Amazon Elastic Cake Store (EBS) or backed by the example shop.
Each AMI includes a template for the root book required for a item type of instance. A typical instance might contain an operating system, an application server and applications. Permissions are also controlled to ensure that AMI launches are restricted to the advisable AWS accounts. Block device mapping ensures that the correct volumes are fastened to the launched instance.
How to create an AMI from an Amazon EC2 instance
Using an Amazon EC2 case, AMIs can be created from running or stopped instances.
- To create an AMI from a running example, users open the Amazon EC2 instances view and right-click on the instance's file to select Create Epitome from the driblet-down menu.
- Subsequently selecting Create Prototype from the drop-downwardly menu, a pop-up window appears with fields requiring information, such as a name and description. Subsequently filling in the field information, select Create Image at the bottom of the window. Amazon EC2 automatically shuts down the instance, takes a snapshot of any volumes attached, creates and registers the AMI, and and then reboots the case. Optionally, No reboot can be selected to foreclose the instance from shutting down.
- The AMI may take a few minutes to exist created. When the creation procedure is consummate, the AMI will appear in the AMIs view in the AWS Explorer. To access the AWS Explorer view, double-click on Amazon EC2 | AMIs node. View AMIs by selecting Owned past Me from the Viewing drop-down list. In that location is a Refresh button to see if the AMI has appeared; if it appears in a awaiting state, it will eventually become available.
Searching for an AMI
Once an AMI is created and registered, it can be used to launch new instances. It's also possible to launch instances from AMIs not belonging to a user if launch permissions are granted by the AMI owners. An AMI tin can be copied into the same or a unlike AWS region, which are the locations where AWS is available. Users tin find an AMI suitable to their case, either provided by AWS, the user community or through the AWS CLI.
AMIs can be selected based on the following factors:
- Region. Users tin can specify which region they want to search for an AMI amid the EC2 locations effectually the world. Locations fall into the categories of Regions (geographic area), Availability Zones (isolated locations within a Region), Local Zones, AWS Outposts and Wavelength Zones. Resource can exist placed in Local Zones to be closer to the end user. AWS Outposts bring any AWS service to information centers or on-premises facilities. Lastly, Wavelength Zones can host applications that provide depression latencies required for communicating with 5G devices.
- Operating organisation. Users can select an AMI image past specifying an operating organisation, such as Linux.
- Compages. The AMI architecture will either be 32-bit or 64-flake depending on the underlying operating system.
- Launch permissions. An possessor decides the launch permission for an AMI, which tin be public (whatever AWS account can get access), explicit (the owner of the AMI provides specific permission to AWS accounts) or implicit (only the possessor has permission to launch the AMI).
- Storage for the root device. Storage for AMIs is either provided by Amazon Rubberband Cake Store (EBS) or by an instance store volume created from a template stored in Amazon S3.
Amazon Linux AMI virtualization types
AWS uses both paravirtualization (PV) and hardware virtual machines (HVM).
- Paravirtualization. This is a virtualization technique that tin improve the performance of invitee operating systems past eliminating the overhead of emulating hardware and by using knowledge of the invitee operating system (OS). It is an approach to virtualization that is effective for high-performance computing (HPC) applications, such every bit those used in scientific computing, transactional databases and other enterprise computing that require rapid processing. PV requires close cooperation between the virtual machine monitor and the guest operating organization, as well as a modified operating system kernel.
- Hardware virtual machines. HVM guests are fully virtualized, and the underlying hardware has to be emulated for the guests to apply. With PV, the guest Bone is modified to run without requiring that emulation. HVM requires that the host machine accept a specific characteristic bachelor on its hardware, whereas PV requires that the invitee Os accept a specific feature present in the software.
While both HVM and PV machines are virtual machines (VMs), the main deviation is that PV virtual machines are lightweight compared to their HVM counterparts. This means a PV VM boots faster and uses less computer hardware but is limited to a smaller number of operating systems.
Ownership, selling and deregistering AMIs
After an AMI is created, it can exist kept private so that merely the owner can use it, or it tin be
shared with specific AWS accounts. AMIs can as well be made public to share with the customs. Using a shared AMI is at the user's risk as Amazon cannot guarantee the integrity or security of publicly shared AMIs by Amazon EC2 users. Shared AMIs should be regarded as whatsoever other foreign code being deployed, meaning that the user is expected to perform their own due diligence earlier using a publicly available AMI.
AMIs tin also be purchased from a third party, including those that come with service contracts from organizations such every bit Ruby-red Chapeau -- a Linux distribution based on the source code of the Linux kernel. Created AMIs tin can also be sold to other Amazon EC2 users.
If an AMI is deregistered, current instances will not be affected, but it cannot be used to launch new instances. Existing instances already using the AMI will not be impacted and will go along to incur instances charges. This ways that when a user is finished with an instance, it should be terminated.
This was terminal updated in June 2021
Continue Reading About Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
- Amazon Linux Container Image on premises is still all about deject
- Amazon Machine Images: HVM or PV?
- Manually spin up an EC2 server instance in vii steps
- Best practices to create and employ Amazon EC2 instances
- A user guide to Amazon Machine Images (AMIs)
Dig Deeper on AWS infrastructure
-

Apply the AWS CLI to create an EC2 instance
-

How to create an EC2 instance from AWS Console
-

Stay online with these 5 AWS disaster recovery best practices
-

Develop an interactive DevOps runbook
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchaws/definition/Amazon-Machine-Image-AMI


